Java Swing
Java Swing tutorial is a part of Java Foundation Classes (JFC) that is used to create window-based applications. It is built on the top of AWT (Abstract Windowing Toolkit) API and entirely written in java.
Unlike AWT, Java Swing provides platform-independent and lightweight components.
The javax.swing package provides classes for java swing API such as JButton, JTextField, JTextArea, JRadioButton, JCheckbox, JMenu, JColorChooser etc.
Commonly used Methods of Component class
The methods of Component class are widely used in java swing that are given below.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| public void add(Component c) | add a component on another component. |
| public void setSize(int width,int height) | sets size of the component. |
| public void setLayout(LayoutManager m) | sets the layout manager for the component. |
| public void setVisible(boolean b) | sets the visibility of the component. It is by default false. |
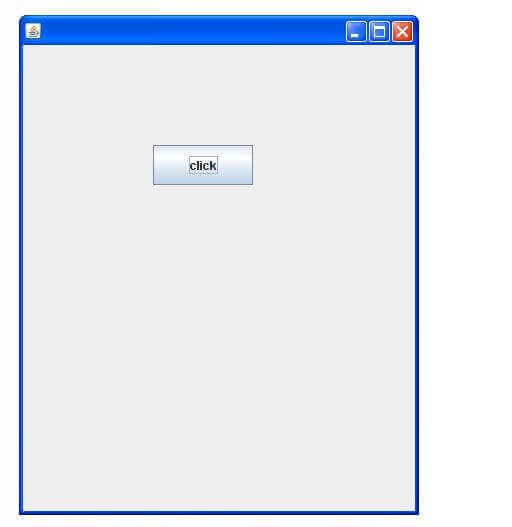
##### Simple Java Swing Example
import javax.swing.*;
public class FirstSwingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame f=new JFrame();//creating instance of JFrame
JButton b=new JButton("click");//creating instance of JButton
b.setBounds(130,100,100, 40);//x axis, y axis, width, height
f.add(b);//adding button in JFrame
f.setSize(400,500);//400 width and 500 height
f.setLayout(null);//using no layout managers
f.setVisible(true);//making the frame visible
}
}
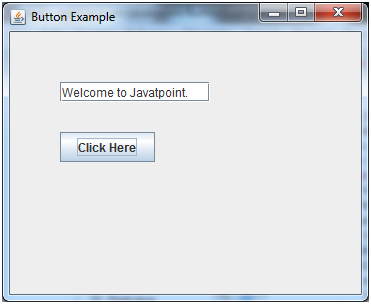
Java JButton Example with ActionListener
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ButtonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame f=new JFrame("Button Example");
final JTextField tf=new JTextField();
tf.setBounds(50,50, 150,20);
JButton b=new JButton("Click Here");
b.setBounds(50,100,95,30);
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
tf.setText("Welcome to Javatpoint.");
}
});
f.add(b);f.add(tf);
f.setSize(400,400);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
Output
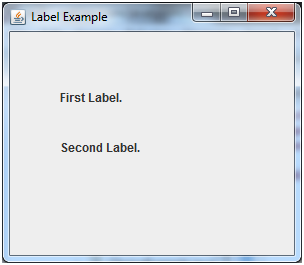
Java JLabel Example
import javax.swing.*;
class LabelExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
JFrame f= new JFrame("Label Example");
JLabel l1,l2;
l1=new JLabel("First Label.");
l1.setBounds(50,50, 100,30);
l2=new JLabel("Second Label.");
l2.setBounds(50,100, 100,30);
f.add(l1); f.add(l2);
f.setSize(300,300);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
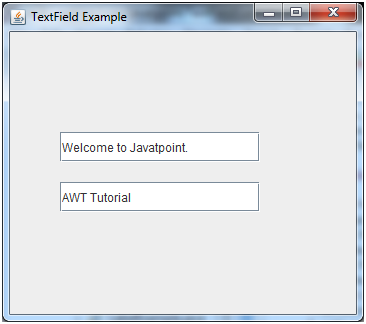
Java JTextField Example
import javax.swing.*;
class TextFieldExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
JFrame f= new JFrame("TextField Example");
JTextField t1,t2;
t1=new JTextField("Welcome to Javatpoint.");
t1.setBounds(50,100, 200,30);
t2=new JTextField("AWT Tutorial");
t2.setBounds(50,150, 200,30);
f.add(t1); f.add(t2);
f.setSize(400,400);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
Output