Java Enums
The Enum in Java is a data type which contains a fixed set of constants.
It can be used for days of the week (SUNDAY, MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, and SATURDAY) , directions (NORTH, SOUTH, EAST, and WEST), season (SPRING, SUMMER, WINTER, and AUTUMN or FALL), colors (RED, YELLOW, BLUE, GREEN, WHITE, and BLACK) etc. According to the Java naming conventions, we should have all constants in capital letters. So, we have enum constants in capital letters.
Java Enums can be thought of as classes which have a fixed set of constants (a variable that does not change). The Java enum constants are static and final implicitly. It is available since JDK 1.5.
Enums are used to create our own data type like classes. The enum data type (also known as Enumerated Data Type) is used to define an enum in Java. Unlike C/C++, enum in Java is more powerful. Here, we can define an enum either inside the class or outside the class.
Java Enum internally inherits the Enum class, so it cannot inherit any other class, but it can implement many interfaces. We can have fields, constructors, methods, and main methods in Java enum.
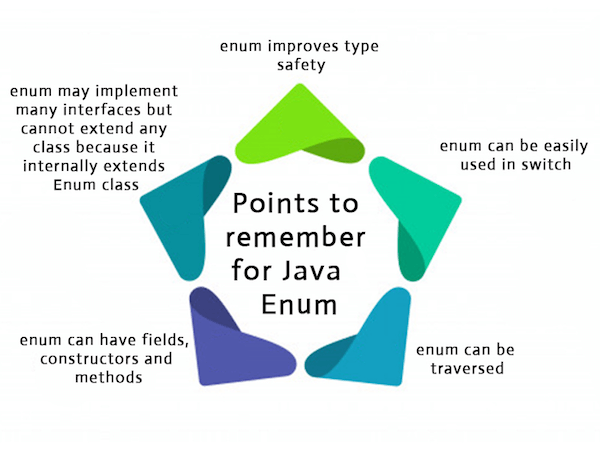
Points to remember for Java Enum
Enum improves type safety
Enum can be easily used in switch
Enum can be traversed
Enum can have fields, constructors and methods
Enum may implement many interfaces but cannot extend any class because it internally extends Enum class
Example
class EnumExample1{
//defining the enum inside the class
public enum Season { WINTER, SPRING, SUMMER, FALL }
//main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
//traversing the enum
for (Season s : Season.values())
System.out.println(s);
}}
Output
WINTER
SPRING
SUMMER
FALL
class EnumExample1{
//defining enum within class
public enum Season { WINTER, SPRING, SUMMER, FALL }
//creating the main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
//printing all enum
for (Season s : Season.values()){
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("Value of WINTER is: "+Season.valueOf("WINTER"));
System.out.println("Index of WINTER is: "+Season.valueOf("WINTER").ordinal());
System.out.println("Index of SUMMER is: "+Season.valueOf("SUMMER").ordinal());
}}
Output
WINTER
SPRING
SUMMER
FALL
Value of WINTER is: WINTER
Index of WINTER is: 0
Index of SUMMER is: 2
Q- What is the purpose of the values() method in the enum?
A- The Java compiler internally adds the values() method when it creates an enum. The values() method returns an array containing all the values of the enum.
Q- What is the purpose of the valueOf() method in the enum?
A- The Java compiler internally adds the valueOf() method when it creates an enum. The valueOf() method returns the value of given constant enum.
Q- What is the purpose of the ordinal() method in the enum?
A- The Java compiler internally adds the ordinal() method when it creates an enum. The ordinal() method returns the index of the enum value.
class EnumExample4{
enum Season{
WINTER(5), SPRING(10), SUMMER(15), FALL(20);
private int value;
private Season(int value){
this.value=value;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
for (Season s : Season.values())
System.out.println(s+" "+s.value);
}}
Output
WINTER 5
SPRING 10
SUMMER 15
FALL 20