Transfer Statement
Java Break Statement
When a break statement is encountered inside a loop, the loop is immediately terminated and the program control resumes at the next statement following the loop.
The Java break is used to break loop or switch statement. It breaks the current flow of the program at specified condition. In case of inner loop, it breaks only inner loop.
We can use Java break statement in all types of loops such as for loop, while loop and do-while loop.
Syntax:
jump-statement;
break;
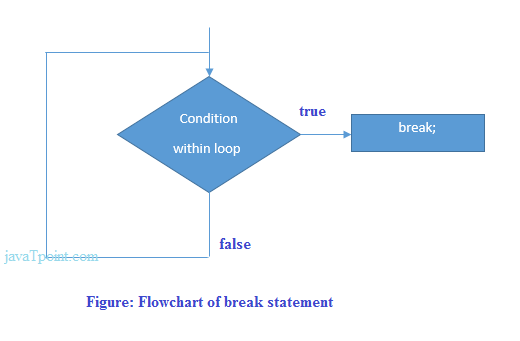
Java Break Statement with Loop
Example:
public class BreakExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//using for loop
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5){
//breaking the loop
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
Output:
1
2
3
4
Continue Statement
The continue statement is used in loop control structure when you need to jump to the next iteration of the loop immediately. It can be used with for loop or while loop.
The Java continue statement is used to continue the loop. It continues the current flow of the program and skips the remaining code at the specified condition. In case of an inner loop, it continues the inner loop only.
We can use Java continue statement in all types of loops such as for loop, while loop and do-while loop.
Syntax:
jump-statement;
continue;
Example
public class ContinueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//for loop
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5){
//using continue statement
continue;//it will skip the rest statement
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
Output:
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10